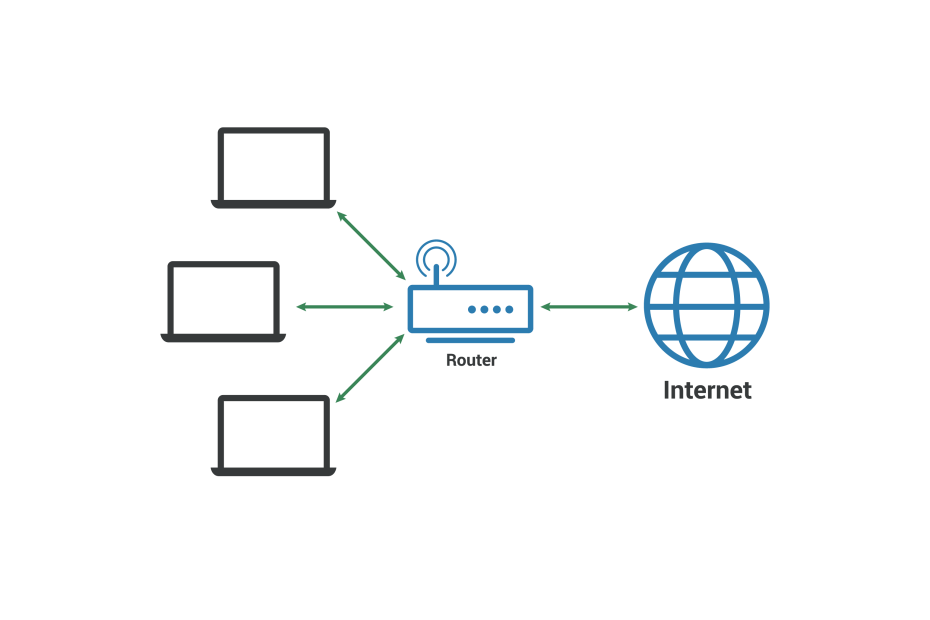
In an ever-growing technological world, we often hear terms such as networks, computer systems, and information technology. A key type of network is a local area network (LAN).
What is a LAN?
A collection of devices connected in one physical location, such as a building, office, or home, is called a local area network (LAN). Depending on its range, a LAN may be small or large, which can typically vary from a small home network with a single user to an enterprise network, with multiple users and devices, such as in offices or schools.
To put it simply, a LAN’s most significant trait is connecting devices that are in a small, limited area. In comparison, a wide area network (WAN) or a metropolitan area network (MAN) covers a much larger geographical region. A network of multiple LANs may also be used to create a WAN or MAN.
Two of the most common technologies used in local area networks are Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
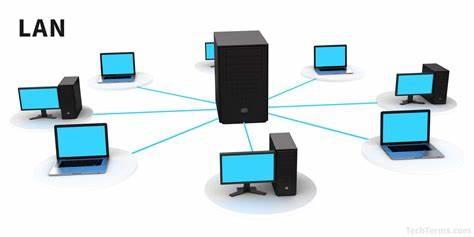
What is in a LAN?
A LAN consists of devices such as access points, cables, routers, switches, and other components. These components enable devices to connect to servers such as internal servers, web servers, and other LANs via wide area networks.
A rise in virtualization has rapidly increased the development and innovation of virtual LANs. With the help of virtual LANs, network administrators can logically link network nodes without major infrastructure changes.
For example, in a college with multiple departments and research facilities, each facility’s computers could logically be connected to the same network but partitioned to behave as if they are separate.
What is the history of LAN?
LANs first emerged in the late 1960s and early 1970s. The first LANs were used in large organizations, such as universities and government agencies, to connect computers and allow them to share resources.
The technology was based on the idea of using a single cable to connect multiple computers, rather than having each computer connected to a mainframe or minicomputer. The first LANs were built using specialized hardware and software and were not widely available to the general public.
In the 1980s and 1990s, LAN technology became more standardized and widely adopted, and Ethernet became the dominant LAN technology. With the advent of the Internet and the proliferation of personal computers, LANs became a common feature in homes and small businesses as well.
What are the benefits of LAN?
Local area networks (LANs) provide several benefits, including:
- Resource sharing: Multiple users may share resources over LAN, such as printers and other files without having to physically transfer them.
- Increased productivity: LANs allow users to connect and share information efficiently, resulting in increased productivity.
- Cost savings: LANs help organizations in saving money by allowing them to share expensive resources, such as servers and software licenses.
- Centralized management: LANs help in the centralized management of resources, and increased security. This helps in keeping track of and protecting sensitive information.
- Scalability: LANs can be easily expanded as an organization grows, allowing it to add more users and devices as needed.
- Remote access: LANs can be connected to other networks, such as the Internet, to allow remote users to access resources and communicate with other users on the LAN.
What are the types of LAN?
There are two primary LAN types: wired LANs and wireless LANs (WLANs).
Wired LAN:-
A wired LAN (Local Area Network) is a type of network that uses Ethernet cables to connect devices such as computers, printers, and servers to share resources and exchange data.
The devices in a wired LAN are connected to a central hub, switch, or router which controls the flow of data and manages the communication between devices. This allows users to share files, access shared printers and other resources, and communicate with each other on the network.
A wired LAN can be set up in a variety of environments, including homes, small businesses, and large organizations. They are typically faster and more secure than wireless networks, but also less mobile and more expensive to install.
Advantages of wired LANs:
- Speed: Wired LANs typically offer faster data transfer speeds than wireless LANs, making them suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications such as streaming video or downloading large files.
- Security: Wired LANs are generally more secure than wireless LANs as it is more difficult to intercept data transmitted over Ethernet cables.
- Reliability: Wired LANs are less susceptible to interference and signal loss than wireless LANs, which can result in a more reliable network connection.
- Easy to Install: Wired LANs are relatively easy to install and set up, and the cables can be run through walls and floors to connect devices in different rooms.
Disadvantages of wired LANs:
- Limited Mobility: Wired LANs require devices to be physically connected to the network, which can limit mobility and make it difficult to work from different locations.
- Cost: Wired LANs can be more expensive to install and maintain than wireless LANs, as Ethernet cables and other hardware can be costly.
- Limited Flexibility: It can be difficult to add new devices to a wired LAN or make changes to the network’s layout without rewiring the entire system.
- Not suitable for portable devices: Wired LANs are not suitable for portable devices such as smartphones and tablets, as they require a physical connection to the network.
Wireless LAN (WLANs):-
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a type of network that uses radio waves to connect devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets to a network without the need for physical cables.
In a wireless LAN, devices connect to a central access point (AP) which controls the flow of data and manages the communication between devices. This allows users to share files, access shared printers and other resources, and communicate with each other on the network.
Wireless LANs can be set up in a variety of environments, including homes, small businesses, and large organizations. They offer more flexibility and mobility than wired LANs as devices can connect to the network without the need for physical cables. They are typically slower and less secure than wired networks, but also less expensive to install and maintain.
Advantages of WLANs:
- Mobility: Wireless LANs allow devices to connect to the network without the need for physical cables, which means users can move around and work from different locations.
- Cost: Wireless LANs are typically less expensive to install and maintain than wired LANs, as there is no need for expensive Ethernet cables and other hardware.
- Flexibility: It is easy to add new devices to a wireless LAN or make changes to the network’s layout without the need to rewire the entire system.
- Suitable for portable devices: Wireless LANs are suitable for portable devices such as smartphones and tablets, as they do not require a physical connection to the network.
Disadvantages of WLANs:
- Speed: Wireless LANs typically offer slower data transfer speeds than wired LANs, which can be a limitation for bandwidth-intensive applications such as streaming video or downloading large files.
- Security: Wireless LANs are generally less secure than wired LANs as they are more susceptible to interference and signal loss, and it is easier to intercept data transmitted over radio waves.
- Reliability: Wireless LANs can be less reliable than wired LANs due to interference and other factors that can affect signal strength.
- Limited range: Wireless LANs have a limited range and the signal strength decreases as the distance between the device and the access point increases, which can lead to connectivity issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that LAN is one of the most important forms of computer networks. The future of LANs (Local Area Networks) will likely involve a continued trend toward wireless networks, as well as the integration of new technologies to improve speed, security, and reliability.
LANs will continue to get faster, more secure, and more reliable with advancements in technology.